The goal of many of our research projects is to understand why customers choose the products or services they do, and to understand why they behave in certain ways.
Helping you understand customer decision making
In business, choices are often driven by multiple factors, such as brand, product features, service features and price.
The problem is knowing which is the key driver to persuade greater take-up of a particular product or service.
What is MAXDIFF?
MAXDIFF is a statistical trade-off technique that quantifies the importance of different product and service benefits on the basis that not all features can be offered to everyone, all the time.
Developed in the early 1990s, and also known as ‘Maximum Difference Scaling’ or ‘Best/Worst Scaling’, MAXDIFF was originally applied to conjoint analysis type problems, but it can also be applied to any type of general scaling of multiple items.
Each MAXDIFF question presents a set of 3 to 5 factors or attributes from which the respondent has to indicate which attribute is most important/most attractive, and which is least important/attractive – see example:
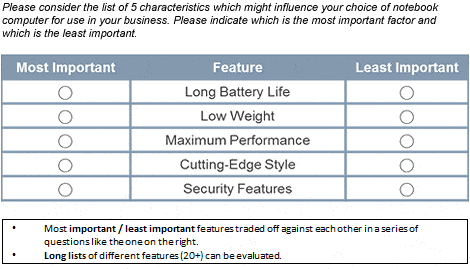
Output from a MAXDIFF project
MAXDIFF projects are useful in that they can help you:
- Understand the importance of specific product/service feature benefits
- Understand the differentiation between key needs – much more than from simple scaler questions
- Group together clusters of the market that have the same requirements
- Create an interactive simulator that allows you to model and predict precisely what different sectors of the market want
Things to consider when designing a MAXDIFF project
- Develop a list of factors or items that you want to test. Ideally, all factors should be worded in the same way to prevent bias. All factors should also be grouped so as not to confuse respondents, i.e, functional benefits of a product tested together and emotional benefits of a product tested together.
- Decide on how you are going to ask the questions. If you are going to ask the questions over the telephone then you need to think about the number of factors to test per question, (this isn’t as much of an issue with self-completion questionnaires).
- Decide how many respondents you want to speak to. This will depend on the number of factors you are looking to test but, in general, if you are looking to test around 20 factors then you would need to speak to a minimum of 100 respondents.


